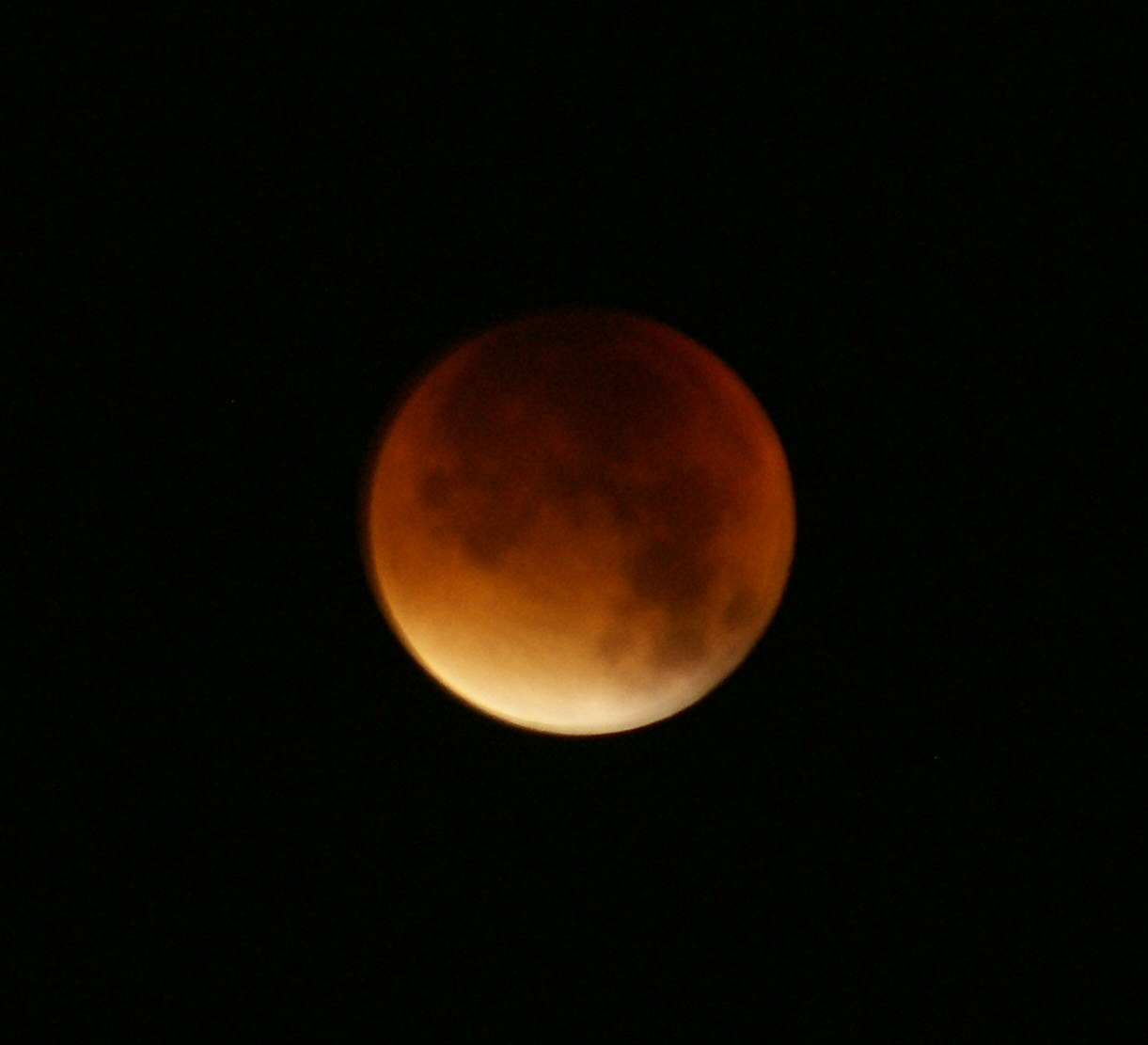



The skies over London were beautifully clear for tonight’s astronomical event. A total lunar eclipse, not exactly a rare event but uncommon enough, coincided rather well with perigee, the Moon’s closest approach to Earth.
A family member with good Greek observed that “peri” means “around” rather than close, making perigee an odd opposite for apogee, but there it is.
In the evening before the eclipse, the full Moon appeared as an exceptionally large, exceptionally bright disk. The rather ridiculous term ‘Supermoon‘ seemed not entirely inappropriate.
A little after 3 am, the moon slipped from the Earth’s penumbra into its umbra and, its disk some 10% larger than usual, appeared to be big and a handsome coppery-orange, in other words distinctly red. The image is in its unadjusted colours, and the camera was as still as I could wedge it, which for a long exposure isn’t saying much, but it gives the feeling of looking for oneself in the middle of the night.
Very gradually the area of brighter yellow-orange at lower left diminished. The Moon’s disk became less and less bright, slowly losing colour. Then equally gradually, an area of brighter yellow-orange started to grow at upper left.
In the evening, the full moon rose between the housetops, a huge, orange-yellow circle, slightly squashed into an ellipse by refraction through the atmosphere. A thin wisp of cloud in the otherwise clear sky gave her yellow glow a ghostly appearance. The moon’s dusty ‘seas’ glowed grey-brown, distinct in outline.
The night was warm. I rose, sticky with sweat, washed, drank, tried to sleep.
A vixen barked, once, twice, faded. I dozed, tried to dream.
The vixen returned, gave her brief yelping bark, louder, nearer, coming closer. I parted the curtain. She was running from left to right along the middle of the road, tail down, nose to ground, shoulders lower than rump, legs moving swiftly in a short trotting gait, grey-brown in the sickly yellow streetlights.
Behind her, on the far pavement, a ghostly shape similar to hers appeared and disappeared, seeming to flicker in the light, vanishing behind the parked cars, more a movement than a shape, her yearling cub, under the vixen moon.
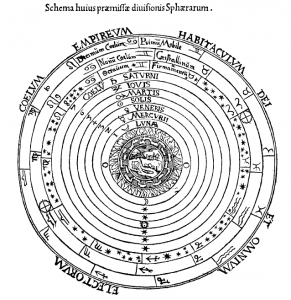
In the Middle Ages, nature – understood as the world of change and decay – stopped at the orbit of the moon; all else above the moon lay in the orbits of the crystalline spheres, culminating in the Empyrean Heavens, the Dwelling Place of God and All the Elect: definitely not ‘nature’ then. The revolution in cosmology and physics brought about by Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo and Newton swept all that away, so today I can happily talk about events in the heavens as natural.
It was spectacular. At 9pm, cloudless night sky was dominated by a brilliant full moon in the southeast, with a brilliant planet – brightly orangey-red in binoculars – just above it. The pundits say the Moon and Mars were just 3 degrees 19 minutes apart. With Mars about as close to Earth as it ever gets, and the moon almost dazzling in the binoculars (it would have been painful through the telescope), it was a fine sight. The ‘planets’ (as they would have said in the Middle Ages) were in the constellation of Virgo, but the moon’s brightness made the background of stars all but impossible to see.
The orbit of Mars is outside the Earth’s, so the planet can appear anywhere around the sky on the ecliptic. The two orbits are both nearly circular, but the planets rotate around the sun at different speeds, so it isn’t often for the two to be close to each other as they are at the moment. And it’s more interesting visually when the Moon is full, its whole disk lit up by the Sun, which means it is opposite the Sun. In other words then, the Sun, Earth, Moon, and Mars are all nearly in a straight line to bring Mars close to Earth, and the Moon to the full position. It doesn’t happen every day.